Everything you need to know about the assistance provided to ESR producer members in 2018.


9,554,164 €
eco-fees paid in 2018
157,647
tonnes marketed in 2018
1,585
member producers in 2018
75%
Operational costs:
management and control of transport, decontamination and recycling operations. R&D investment.
21%
Operating costs:
salaries and organisational costs.
4%
Information:
waste prevention and incentive to recycle campaigns.
In accordance with its obligations in the specifications document for authority approval, ESR checks more than 15% of the tonnages declared by its producer members. This independent audit checks that the information reported is correct and is compliant to the reference information provided by ESR, based on the fee scale and guide documents. It also allows any errors observed in the reporting to be identified and measured.
Any sticking points, misunderstandings or points requiring further clarification to improve reporting quality are given special attention as are producer best practices. The understanding and the application of the reference information in the 20 companies audited were assessed using the declarations on the introduction of equipment onto the market from 2015 to 2017.
After these audits have been completed, each member receives a report in order to better understand and implement the methods in declaring information and its correction. Among best practices recorded, the implementation of internal audits and the existence of reference information in order to complete reporting declarations are strengths within the companies audited. However, due to the wide variety and modularity of equipment the identification of the scope still needs to be improved along with the regular updating of the articles and area concerned by regulations. In 2018, the differences in declared and observed tonnages amounted to 283 tonnes over the 3 years audited.

Launched three years ago by Eco-systèmes and Récylum, the only European database evaluating the environmental impact of electrical and electronic equipment at the end of their service life, was finished in 2018. With eight new equipment streams added, 86 materials have now been modelled and rolled out according to the different streams treated enabling manufacturers to quantify the environmental impacts and benefits of their design choices during the recycling of their equipment.
Created to incite, facilitate and encourage eco-design, the data provided to manufacturers allows them to assess the environmental impacts of their electrical equipment’s end-of-service life according to its composition. Thanks to the database, made freely available to all stakeholders in the sector by ESR, it is now possible to act effectively in the choice of materials according to their impacts at the end of their service life.
Accessible to producers, the database is in particular aimed at Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) software users. By integrating new data into these tools, the end-of-service life of appliances can be quickly, reliably and representatively modelled. This data has been integrated into widely known life cycle analysis software, such as EIME, SimaPro, etc.
Some professional streams such as large equipment from the medical sector, construction, research and industry have been added to the database in 2018 as well as small air conditioning equipment. Other types of equipment such as professional lighting equipment, power converters, industrial electrical motors, rooftop air conditioners, commercial cooling appliances and drinking water fountains have also been newly referenced.
To guarantee good representativeness of this data, Eco-systèmes and Récylum have modelled all end-of-service life processes for equipment at more than 50 WEEE (Waste Electric and Electronic Equipment) decontamination and treatment sites as well as for fifteen recovery or disposal processes.
The database is now even more exhaustive than ever before because it alone has 950 Life Cycle Inventories (LCI) that can be downloaded via the European platform “Life Cycle Data Network” (LCDN), developed by the Joint Research Centre (JRC), the European Commission’s research centre. The data is available on: http://weee-lci.recylum.com
ESR continues to raise awareness and assists its producers in the recyclability of their products by taking into account the “end-of-service life” challenges during the design stage of their new appliances as well as the integration recycled plastics (8 projects in 2018).
In addition to direct meetings with producer members, ESR also participated in the following events:
ESR also organised 7 visits and eco-design workshops with producers and retailers.
ESR is co-steering works on two future European standards. The 1st focuses on evaluating an appliance’s recyclability and potential recovery. By monitoring this standard ESR is able to ensure that its REEECYC’LAB tool, made available to producers, is methodologically aligned. The 2nd focuses on evaluating the recycled materials content of appliances. These works started in 2015 by the European Standardisation Committee and should be completed by 2020. Several producer members and ESR partner operators are also involved in establishing these standards.
Furthermore, ESR is also monitoring a European standard which is currently being developed, the purpose of which is to set common rules on using life cycle analyses, enabling, in fine, environmental reporting declarations to be completed for equipment.
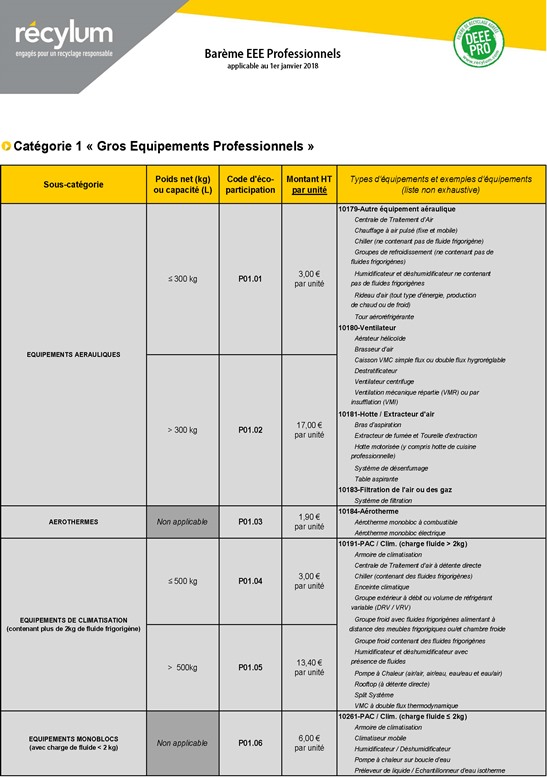
Since the middle of 2018, ESR examined the possibility of modulating the professional equipment eco-fee scale, for all categories. Comprising professional organisations from the different professional equipment sectors, recycling operators and industrials, a specific working group was created to examine the possibility of such a modulation system, of its opportunities and its restrictions.
The first results of the study have already been presented to the working group in March 2019, then to the DGPR and the DGE. Work is still ongoing to determine the families of products concerned by the bonus/penalty system as well as the modulation retained (recyclability, extension of service life, decontamination, etc.).
In 2018, ESR established a single portal for EEE producers. ESR producer members declaring several types of equipment (household, professional, lamps and small fire extinguishers) can now complete their declarations on line using a single entry point. This portal is the first tangible element in the simplification of services desired by the merger.
Furthermore, the Eco-systèmes and Récylum fee scales have been streamlined following their merger within ESR. Also, since 15 August. with “open scope”, new categories have been integrated into the professional WEEE sector with the arrival of categories 12 and 13.